
:quality(90)/f/60990/750x420/d6a707e578/relative-pronoun.png)
In the first sentence, what subordinates the clause what she wants. Indefinite relative pronouns include words such as what, where, whoever, whomever, whichever, and whatever.Ĭarla asked Tanille where she went for dinner.Īaron wants the boat so much he said he’s willing to pay whatever they ask for it.
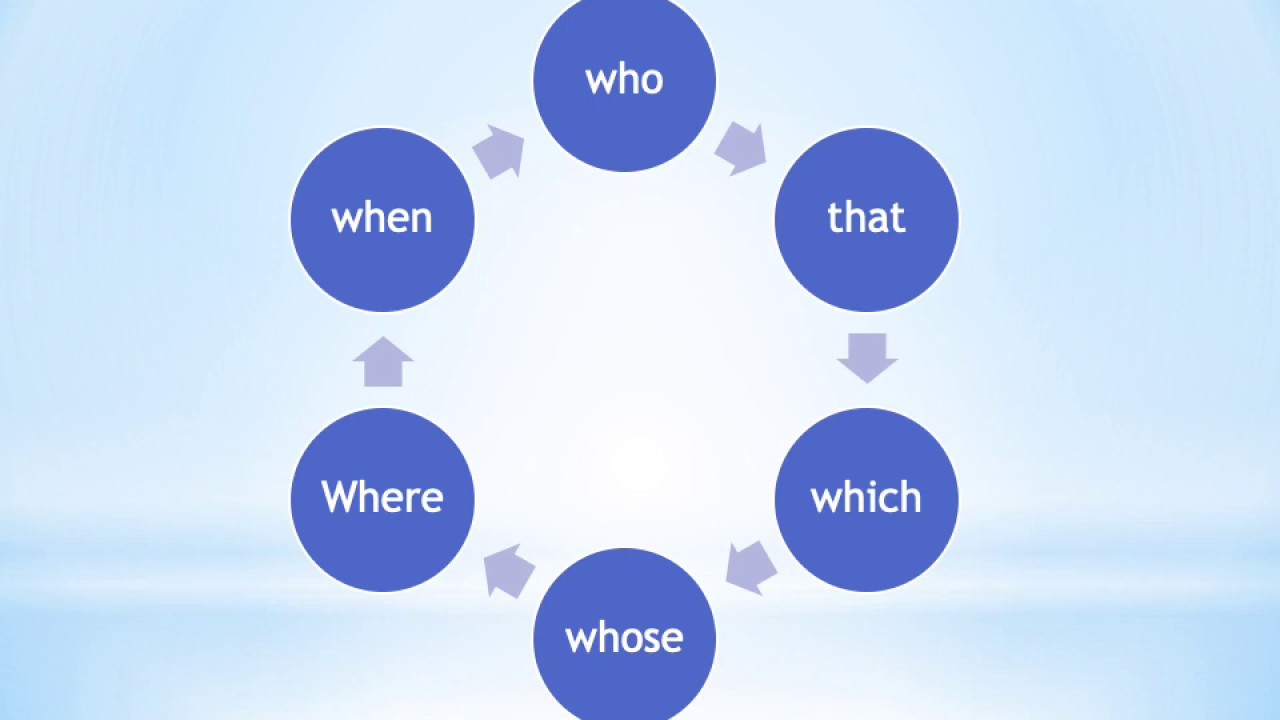

Some relative pronouns do not modify a noun antecedent rather, they operate as indefinite relative pronouns that introduce a clause functioning as a subject or object noun. Sheila held tightly to the dog whose companionship had never waned.Įach sentence has a subordinate clause marked by a relative pronoun that further describes a noun ( daughter > who, car > that, dog > whose). I want the car that gets the best mileage per gallon. He has a daughter who is a talented ice skater. They typically refer to people, places, animals, things, or ideas. The relative pronouns are that, which, who, whom, and whose. You might hear it called an adjective clause as well because it tells us more about a noun- the pronoun’s antecedent-in the main clause. Relative Pronouns: What Is a Relative Pronoun?Ī relative pronoun substitutes for a noun to introduce a subordinate (dependent) clause, which is one that must be joined with an independent (main) clause to complete the sentence in which it appears.Ī dependent clause led by a relative pronoun is also referred to as a relative clause.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
